After projecting a positive variance of $3 million for the 2021 budget year, it would appear the final tally for a budget surplus for 2021 will be coming in at $5.6 million. Thunder Bay will have its seventh consecutive positive budget variance making for accumulated variances of $26 million over seven years. Much of the savings will come from lower-than-expected COVID costs for which the city has received a lot of federal and provincial support. While Thunder Bay budgeted for a $7.2 million cost from the COVID-19 pandemic this year, a third quarter variance report now forecasts COVID costs at $5.5 million, based on trends to the end of September.
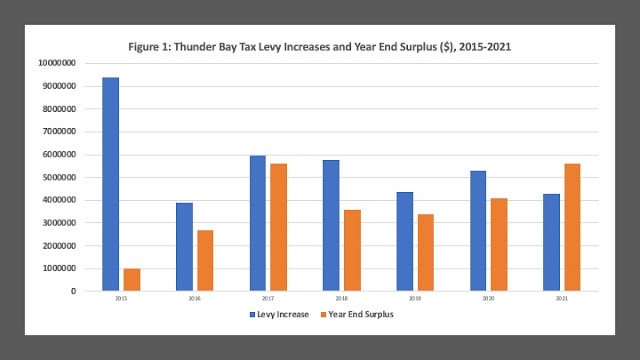
Figure 1 plots the annual tax levy increase since 2015 against the corresponding surplus at year end. For example, in 2015, the tax levy increase was $9.4 million – a 5.7 percent increase on a $164.7 million levy the year previous. The year’s end saw a positive variance of about $1 million which on $174 million tax levy was just over one-half of one percent. Since 2015, however the size of the surplus has increased substantially, often coming close to matching the size of the tax levy increase that year. In 2017 for example, the levy increase was $5.96 million – a 3.3 percent increase – but the year-end surplus came in at $5.6 million – almost 95 percent of the value of the original levy. For 2021, we have a first – a surplus of $5.6 million – which is larger than the original levy increase of $4.3 million.
The surplus is generally put into city reserve funds which in general is a prudent strategy. However, the fact that there are consistent surpluses means that there has been a consistent practice of overestimating expenditures and underestimating revenues. Given that the tax increases have been much larger than what was required given the ultimate need, one can only conclude that this has become a sort of forced savings strategy. The City of Thunder Bay raises the tax levy more than is needed with the goal of boosting its reserves for whatever long-term plans they might have for spending from those reserves.
Thunder Bay has been raising taxes consistently more than it has needed to for some time now and that money comes out of the pockets of its residents. During the pandemic, while other cities were trying to keep tax increases at zero, Thunder Bay managed an increase of 2.7 percent in 2020 and 2.1 percent in 2021. Accompanied by generous provincial and federal COVID-19 support, the result has been large and growing surpluses.
One could pose the following counterfactual. If Thunder Bay had been able to anticipate the surplus each year and implement a tax increase incorporating the surplus and balancing the budget, what would have the alternate tax levy increase have been? Figure 2 plots the actual percentage tax levy increase since 2015 and the alternate increases. In 2017, for example, the budget could have been balanced with an increase of 0.2 percent but instead there was an increase of 3.3 percent. Last year – 2020 - saw an increase of 2.7 percent but all that was needed is an increase of 0.6 percent. Meanwhile, if 2021 continues on this track, it means that rather than a 2.1 percent levy increase, there could have been a levy reduction of nearly 1 percent.
So, here is the thing. Over the period 2015 to 2021 the actual tax levy increase has averaged 3.1 percent. The average levy increase required to meet expenditures has been 1.1 percent. City council for 2022 has directed administration to prepare a municipal budget with a 2.25 percent levy increase. I would suggest that based on the City’s financial performance to date that they could easily cut that in half. One percent sounds about right.